Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention
Acne is one of the most common dermatological conditions worldwide, affecting millions of adolescents and adults. Although often viewed as a cosmetic issue, acne can significantly impact self-esteem, emotional well-being, and quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, available treatments, and effective prevention methods is essential for achieving clearer and healthier skin.
This comprehensive guide explains everything about acne from a medical perspective, including SEO-friendly keywords such as acne treatment, acne causes, how to get rid of acne, acne scars, hormonal acne, best skincare for acne, and more.
What Is Acne?
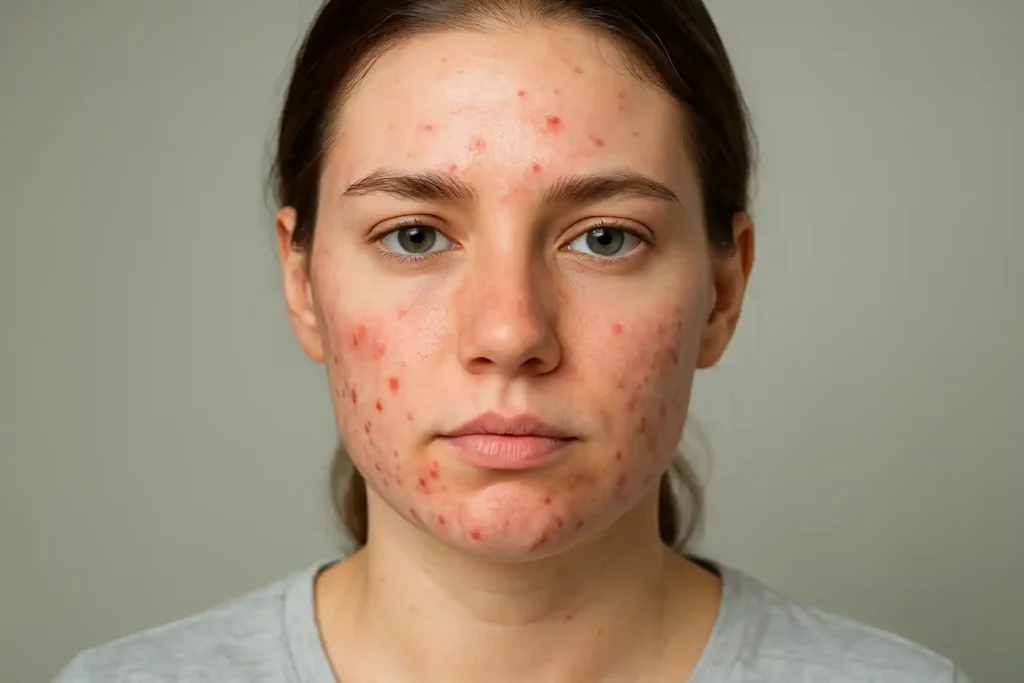
Acne is an inflammatory skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with excess oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. It typically appears on the face, chest, shoulders, and back—areas with a high concentration of oil glands.
Main Types of Acne Lesions
Comedones:
Blackheads: Open pores with oxidized oil
Whiteheads: Closed pores underneath the skin
Papules: Small, red, inflamed bumps
Pustules: Pimples with visible pus
Nodules: Large, painful lumps deep in the skin
Cysts: Severe, pus-filled lesions that can leave scars
Understanding the type of acne is essential for choosing the right treatment.
What Causes Acne?
While many people believe acne is caused by poor hygiene, the real causes are more complex and biological.
1. Excess Sebum Production
Sebaceous glands produce oil to protect the skin. Hormonal fluctuations—especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or stress—increase sebum production and clog pores.
2. Clogged Hair Follicles
Dead skin cells should shed naturally, but in acne-prone skin they stick together, forming plugs inside the follicle.
3. Bacterial Overgrowth
Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) thrives inside clogged pores, causing inflammation and infection.
4. Hormonal Changes
Known as hormonal acne, this type is common in:
Women with PCOS
Teens
People under stress
Individuals experiencing hormonal imbalances
Hormones stimulate oil production, increasing the risk of acne flare-ups.
5. Genetics
Acne tends to run in families. If one or both parents had severe acne, the likelihood of developing it increases.
6. Lifestyle Factors
High-glycemic diet (sugary foods, white bread, pastries)
Dairy consumption in some individuals
Poor-quality skincare products
Stress and lack of sleep
Certain medications (steroids, lithium, etc.)
Common Symptoms of Acne
Symptoms depend on severity, but often include:
Pimples and bumps
Redness and inflammation
Oily skin
Painful nodules
Scarring or dark spots (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation)
Acne may also have emotional symptoms such as anxiety, low confidence, and social withdrawal.
Medical Treatments for Acne
The best acne treatment depends on the severity and type.
1. Topical Medications
Dermatologists often begin with topical treatments:
Benzoyl Peroxide
Kills acne-causing bacteria
Reduces inflammation
Helps in mild to moderate acne
Retinoids (Adapalene, Tretinoin)
Increase cell turnover
Prevent clogged pores
Reduce the appearance of acne scars over time
Azelaic Acid
Anti-inflammatory
Good for sensitive skin
Helps treat hyperpigmentation
Topical Antibiotics
Clindamycin or erythromycin
Usually combined with benzoyl peroxide to prevent resistance
2. Oral Medications
For moderate to severe acne, doctors may prescribe:
Oral Antibiotics
Doxycycline or minocycline
Reduce inflammation and bacterial overgrowth
Hormonal Treatments
Birth control pills
Spironolactone (reduces androgen activity)
Highly effective for hormonal acne in women.
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
The strongest acne medication available
Often used for cystic or treatment-resistant acne
Can produce long-term remission
Natural and Home-Based Treatments
While medical treatments are the most effective, natural options can help support improvement:
Tea Tree Oil
A natural antibacterial agent effective for mild acne.
Zinc Supplements
Reduces inflammation and supports healing.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Beneficial for reducing inflammation from the inside out.
Green Tea Extract
Contains antioxidants that help regulate oil production.
Healthy Diet for Acne
Some foods that can help:
Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants
Foods high in omega-3 (salmon, walnuts, chia seeds)
Probiotics (yogurt, kefir, supplements)
Foods to avoid in acne-prone individuals:
Sugary snacks
Processed foods
Excess dairy
Greasy fast food
Acne Scars: Types and Treatments
Acne scars occur mostly after severe inflammation.
Types of Scars
Ice-pick scars
Boxcar scars
Rolling scars
Dark spots (hyperpigmentation)
Treatments
Chemical peels
Microneedling
Laser therapy
Dermal fillers
Topical retinoids
Treating scars often requires multiple sessions and professional evaluation.
Prevention: How to Reduce Acne Flare-Ups
Consistent skincare is crucial.
1. Use Non-Comedogenic Products
These products are specially formulated not to clog pores.
2. Wash Your Face Gently
Over-washing can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
3. Avoid Touching Your Face
Hands carry bacteria that can trigger breakouts.
4. Stay Hydrated
Water supports overall skin health and healing.
5. Manage Stress
Stress hormones increase oil production, leading to more acne.
6. Keep Hair Away from the Face
Hair products and oils can cause forehead and cheek acne.
SEO-Optimized Keywords to Include in Your Post
To help your article rank on Google, here are SEO keywords to use naturally throughout:
acne causes
acne treatment
how to get rid of acne
hormonal acne
natural remedies for acne
acne skincare routine
acne prevention tips
best products for acne
acne scars treatment
Integrating these terms will help increase visibility and search performance.
When to See a Dermatologist
Seek professional help if:
Acne is severe or painful
Over-the-counter treatments don’t work
Scarring begins to appear
Acne affects your confidence or emotional well-being
A dermatologist can create a personalized treatment plan that delivers long-term results.
Acne is a complex skin condition influenced by hormones, genetics, bacteria, and lifestyle. While it can be frustrating, modern dermatology offers highly effective treatments—from topical medications to oral therapies and advanced procedures for scars. With consistent care, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance, clearer skin is achievable for most individuals.
Whether you suffer from occasional breakouts or severe cystic acne, understanding the condition is the first step toward long-term skin health and confidence.